Knee Pain Treatment
What can I do about my knee pain?

Lifestyle changes
Losing weight if needed & taking more exercise.
Physical Management
Having physiotherapy & occupational therapy (OT). This may include using walking aids or special insoles.
Pain Medication
Treatments to manage pain, including tablets you take by mouth, injections into the joint and self-help support.
Surgery
Surgery, including total or partial knee replacement, arthroscopy & osteotomy. Surgery is usually for people with severe symptoms who have tried other treatments first.
Getting an Expert Opinion
You've been suffering with knee pain & it's affecting your quality of life and day to day activity.
You may have been taking pain relief, visited your G.P. or physio & have now decided you would like to see an expert for advice.

Initial Consultation
Follow up Consultation
Follow up Consultation
I would see you for an initial consultation and during the appointment we will discuss your knee pain & I will examine your knee. You may be recommended various options such as needing an x-ray or MRI scan.
Next steps to help with your knee pain maybe advised such as pain relief medication, exercise or phyiostherapy, losing weight or surgery.

Follow up Consultation
Follow up Consultation
Follow up Consultation
You may like to have a follow up appointment to see how your knee is progressing after a length of time or if you have tried losing weight, exercising or various treatments, but you're still in pain.
You may have decided to have knee surgery.

Surgery
Follow up Consultation
Surgery
It maybe decided that surgery is this best route for the treatment of you knee pain. This may be a partial or total knee replacement. You would come for a pre -op assessment a few weeks before your surgery. After the operation you will require a few days stay in hospital to recover. I will be monitoring your progress & you will asked to come back in around six weeks time for your post-op consultation to see how you are going.
Knee Replacement Surgery
What is knee replacement surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is a highly successful operation for knee arthritis. It can significantly improve the quality of your life. Knee replacements are now performing extremely well.
Knee replacements resurface the worn ends of the knee joint. The metal implants are cemented in place using special bone cement. Between the two metal implants there is a hard wearing plastic insert.
Depending upon your type of arthritis, you may be suitable for either a partial or total knee replacement.
Total knee replacements resurface the entire knee joint, while partial knee replacements only replace the worn side.

Total Knee Replacement Surgery
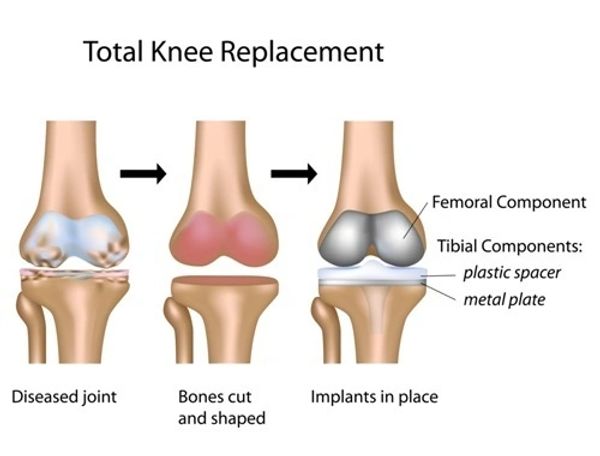
Knee replacement surgery is a highly successful operation for knee arthritis. It can significantly improve the quality of your life. Knee replacements are now performing extremely well. Approximately 80% of knee replacements now last over 25 years.
Total knee replacement surgery resurfaces the entire knee joint. Both ends of the joint are replaced with metal implants that are cemented in place using special bone cement. The worn surface of the kneecap (patella) is resurfaced using a plastic button.
I routinely use the Triathlon knee replacement by Stryker which has an excellent long term track record and is outperforming most other implants.
I am a high volume knee replacement surgeon and speciailse in this operation. I regularly teach on courses teaching other consultants how to perform this surgery.
Total knee replacement surgery may be performed using manual or robotic techniques.
Partial Knee Replacement

Partial knee replacement is where only one of the compartments of the knee is replaced, most commonly the inside (medial).
If most of your pain is in the inside of your knee, you may be suitable for partial knee replacement surgery.
The advantages of partial knee replacement surgery are that you often have a more 'normal' feeling knee, and the surgery is less invasive, so often only one night is hospital is required, or may even be able to be performed as a day-case operation.
The risks are generally lower and most still last very well. The latest evidence shows that around 70% of partial knee replacements last over 25 years.
Partial knee replacement surgery may be performed using manual or robotic techniques.
Mako Robotic Knee Surgery
Mako robotic surgery has been available in Exeter since 2016. I am part of the senior teaching team teaching surgeons to perform robotic surgery around Europe.
Robotic surgery has the potential advantage of performing your surgery more accurately and with a higher level of precision. A CT scan is performed of your knee, which allows a level of precision during surgery to less than half a millimetre. Advanced planning software enhances surgical planning, intra-operative adjustment can be performed during the surgery and the robotic arm is able to deliver the plan accurately and safely.
I believe that robotic surgery has the potential to improve outcomes from knee replacement surgery, and the Stryker Mako robot is the most advanced surgical robot available.
Feel free to speak to me about whether you may be suitable for Mako robotic surgery.
Robotic knee replacement surgery is now available at the Exeter Nuffield Hospital, the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital and the Exeter Nightingale Hospital (SWAOC)



Receive a Specialist Opinion
I work alongside other experienced colleagues at the Exeter Knee Reconstruction Unit at the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital. As a group, we provide advice and support to surgeons in the South West Peninsula for patients with complex problems of the knee.
I work closely with my colleagues and we frequently work together, discussing complex cases and planning surgeries. As part of our routine practice we hold weekly Multi-Disciplinary Meetings at the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital to plan and discuss cases, teach colleagues and provide advice.

What happens when I'm listed for Knee Surgery?
Consultation in Clinic
Pre-Operative Assessment
Pre-Operative Assessment

In the clinic Mr Phillips will take a thorough medical history, perform an examination and Xrays will be taken. A detailed conversation will take place where the risks and benefits of the surgery will be discussed and you will be given the opportunity to ask any questions you may have.
Pre-Operative Assessment
Pre-Operative Assessment
Pre-Operative Assessment

After being given a date for surgery, you will attend a pre-op assessment appointment to ensure that you are fit for surgery.
Please bring along with you a list of your medications and other health conditions.
Meet the Anaesthetist
Pre-Operative Assessment

You will be admitted on the day of the operation. You will be seen prior to surgery by the anaesthetist. Mr Phillips' routine practice is for his patients to have a spinal anaesthetic (where the legs are made numb). At the same time, If you would like, you can be made sleepy so you are completely unaware of the surgery. Mr Phillips also performs a local anaesthetic injection at the time of surgery to improve your post-operative pain relief. We have found that this is the best way to have the surgery causing the least discomfort.
Resurfacing the Knee

During knee replacement surgery, the worn surface of the bone is removed and replaced with an implant that is cemented in place. On the tibial side, the implant is made of metal (usually cobalt chrome or titanium, depending upon the implant). On the femoral side, the implant is made of cobalt chrome and is shaped to fit onto the end of the bone. Between the two metal components, a plastic (ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene) is placed so that there is no contact between the metal components (so there is no concern about metal on metal implants in knees). Usually the worn under-surface of the knee cap is also resurfaced using a plastic button cemented in place.
Placement of Implant
Placement of Implant

The knee replacement is positioned in your knee to fit the way that you are made. Precise checks are made to confirm that everything is stable prior to the final implants being cemented in place. The aims of surgery is to give you a stable, straight knee.
Recovery
Placement of Implant

You will wake up in the Recovery Room and be transferred to the ward once you are ready. You will be seen on the ward by the physiotherapist the day after surgery where you will start getting the knee moving and you will be able to walk with support. The average length of stay is one to two days in hospital.
After the operation the knee is quite stiff and uncomfortable as you recover from surgery. This does improve and normally patients are able to walk free from crutches at about the six week stage. Patients are advised not to drive for the first six weeks after surgery.
Knee Arthroscopy Surgery

Knee arthroscopy is keyhole surgery of the knee. Using advanced arthroscopic techniques, tears to the meniscus can be debrided or repaired and small areas of worn cartilage can be treated using chondroplasty or microfracture.
The most common reason for knee arthroscopy is to treat a meniscal tear (known as the sport cartilage). These most often occur on the inside (medial) part of the knee. Tears in the meniscus can sometimes happen after a bad twist of the knee, but they can sometimes occur without any history of an injury. Meniscal tears can cause pain, swelling, jamming or locking and sometimes the feeling that the knee wants to give way.
There is some good evidence that many meniscal tears get better on their own within three to six months. However, if symptoms continue to persist or cause significant problems then arthroscopy of the knee can treat these symptoms quite reliably. Usually a procedure called debridement (where the torn edges are trimmed away) is performed. In cases of large tears, especially in younger patients, meniscal repair can be performed using small sutures inside the knee.
What happens when I'm listed for Knee Arthroscopy?
Consultation in Clinic
Pre-Operative Assessment
Pre-Operative Assessment

In the clinic Mr Phillips will take a thorough medical history, perform an examination and Xrays will be taken. A detailed conversation will take place where the risks and benefits of the surgery will be discussed and you will be given the opportunity to ask any questions you may have.
Pre-Operative Assessment
Pre-Operative Assessment
Pre-Operative Assessment

After being given a date for surgery, you will attend a pre-op assessment appointment to ensure that you are fit for surgery.
Anaesthetic
Pre-Operative Assessment

You would be seen by the anaesthetist and normally given a general anaesthetic.
Surgery
Recovery

Arthroscopy is usually performed as a day case procedure. You would be seen by the anaesthetist and normally given a general anaesthetic.
Recovery
Recovery
Recovery

After the operation you will have a bandage on the knee. You will be encouraged to stand and walk. You will be offered crutches and allowed home after a few hours. Symptoms usually improve straight away, however it may take up to 6 weeks to gain the full benefit of surgery.